RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION
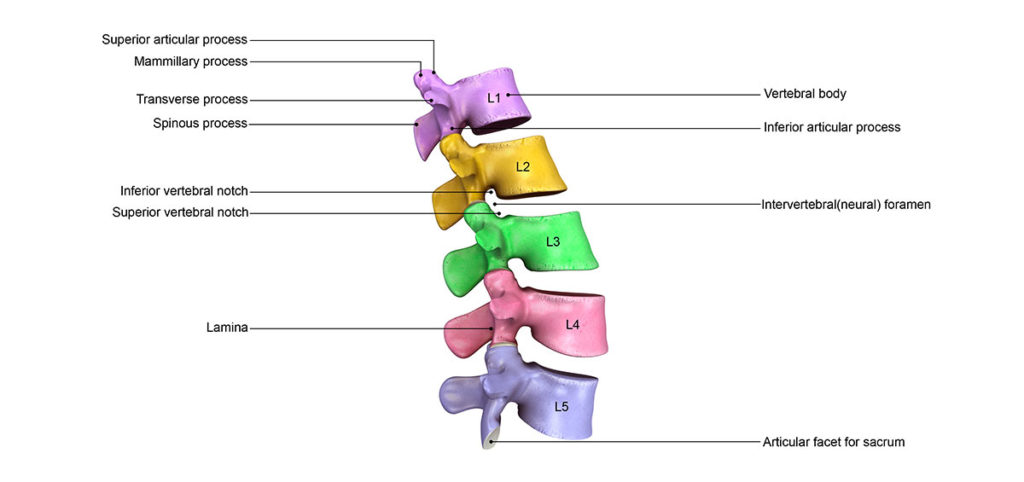
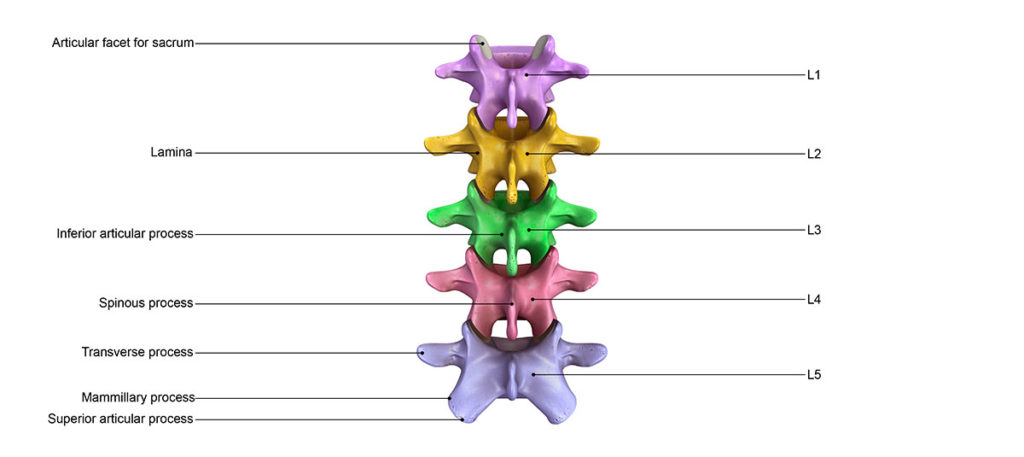
Facet joints are paired structures at the back of each vertebral bone in the spinal column. The facet joints allow movement between neighboring vertebrae, and can be a source of pain due to spinal arthritis (spondylosis), post-traumatic pain (whiplash), and many other conditions. In order to determine if a patient is a good candidate for radiofrequency ablation, a “trial” diagnostic block is performed, which is known as a medial branch block (MBB).
If the patient experiences significant relief with the MBB procedure, s/he may be a good candidate for radiofrequency ablation (RFA). Radiofrequency ablation uses heat energy created by ultra-high frequency electromagnetic waves, to selectively destroy the nerves that carry pain impulses from the facet joints to the brain. Pain can be reduced or eliminated for up to 12 months, at which time the procedure may be repeated, if needed.
Radiofrequency ablation can be performed for the facets joints in the neck (cervical), torso (thoracic) and lower back (lumbar) regions. Side effects are mild, and may include pain at the injection sites and temporary worsening of symptoms.
- If you are taking a blood thinner, please call your primary care physician or cardiologist and ask if it is safe to stop the medication. They will instruct you on how to stop it when it is time for your injection. This will decrease the likelihood of bleeding complications.